Strategic deployment of riparian buffers and windbreaks in Europe can co-deliver biomass and environmental benefits
Communications Earth & Environment, available open access here
Within the scope of the new Common Agricultural Policy of the European Union, in coherence with other EU policies, new incentives are developed for farmers to deploy practices that are beneficial for climate, water, soil, air, and biodiversity. Such practices include establishment of multifunctional biomass production systems, designed to reduce environmental impacts while providing biomass for food, feed, bioenergy, and other biobased products. Here, we model three scenarios of large-scale deployment for two such systems, riparian buffers and windbreaks, across over 81,000 landscapes in Europe, and quantify the corresponding areas, biomass output, and environmental benefits. The results show that these systems can effectively reduce nitrogen emissions to water and soil loss by wind erosion, while simultaneously providing substantial environmental co-benefits, having limited negative effects on current agricultural production. This kind of beneficial land-use change using strategic perennialization is important for meeting environmental objectives while advancing towards a sustainable bioeconomy.
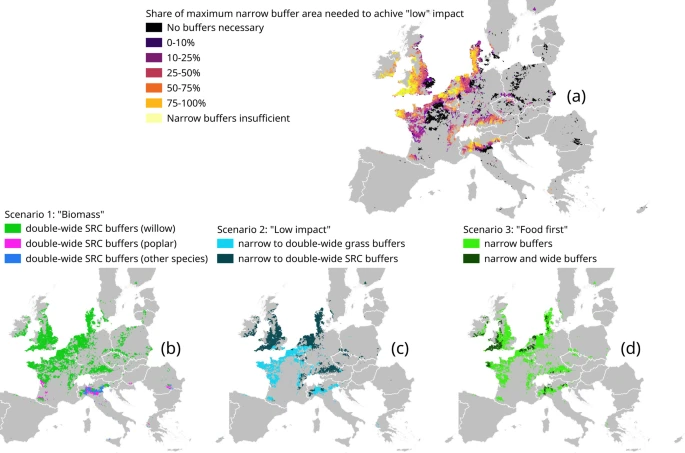
Share of maximum narrow buffer area needed to achieve a low level of nitrogen emissions to water (a), and the type of riparian buffers established in the three deployment scenarios (b–d). See “Methods” for information about what determines the buffer type in each landscape and scenario.


